| SOFTWARE IN PRACTICE |
|
Traceability Analysis(Alias: Traceability Matrix)
We shall not cease from exploration Traceability is a property of an element of documentation or code that indicates the degree to which it can be traced to its origin or "reason for being". Traceability also indicates the ability to establish a predecessor-successor relationship between one work product and another. A work product is said to be traceable if it can be proved that it complies with its specification. For example, a software design is said to be traceable if it satisfies all the requirements stated in the software requirements specification. Examples of traceability include:
Traceability analysis is the process of tracking forward or backward through a network of interrelationships between components of a system and their documentation to establish that:
The outcome of traceability analysis is typically a traceability matrix. The figure provides an example of the various classes of analysis that can be performed to establish the traceability of a Software Architecture Design Description. Tracing a Software Architecture Design Description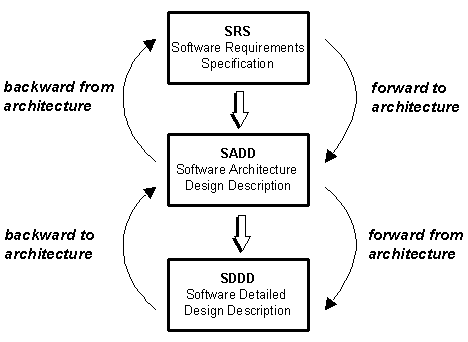
In this case the four classes of traceability reveal the following insights: Backward from architecture
Forward to architecture
Backward to architecture
Forward from architecture
Given the complexity of most software products, traceability matrices are produced with automated tools such as:
|

|