Hazard Analysis
(Alias: PHA, Preliminary Hazard Analysis)
Replicants are like any other machine. They're either a benefit or a hazard. If they're a benefit, it's not my problem.
- Deckard, From the Movie Blade Runner, Director: Ridley Scott
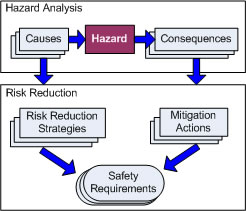
Hazard analysis is the process of recognizing hazards that may arise from a system or its environment, documenting their unwanted consequences and analyzing their potential causes. The hazard analysis process commences with a Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) in the early stages of a project and continues throughout the system product's life cycle. |
|
International standards define hazard analysis as follows:
- The process of describing in detail the hazards and accidents associated with a system, and defining accident sequences1.
- Identify hazards through a systematic hazard analysis
process encompassing detailed analysis of system hardware and software, the environment (in
which the system will exist), and the intended use or application. Consider and use historical
hazard and mishap data, including lessons learned from other systems. Identification of hazards
is a responsibility of all program members. During hazard identification, consider hazards that
could occur over the system life cycle2.
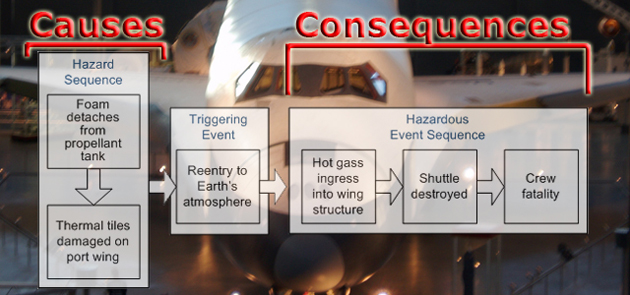
Hazard Analysis Objectives ⇑
The objectives of a hazard analysis are to:
- Identify hazards. To determine the hazards and hazardous events of the equipment under control and the control system (in all modes of operation), for all reasonably foreseeable circumstances including fault conditions and misuse
- Identify causes. To analyse the event sequences leading to the hazardous events identified
- Determine risks. To analyse the risks associated with the hazardous events.
|
 |
A hazard analysis might be performed in one of the following contexts:
- Development. Examining a system in development to identify and assess potential hazards and eliminate or control them
- Operations and management. Examining an existing system to identify and assess hazards in order to improve the level of safety; formulating safety management policy; training personnel; increasing motivation for efficiency and safety of operation
- Certification. Examining a planned or existing system to demonstrate its level of safety and to facilitate acceptance by a customer, a government safety authority or the public.
The synthesis of a safe design does not guarantee a safe working system. Hazard analysis is therefore an iterative process that continues for the life of a system. The objective of progressive hazard analysis is therefore to identify and mitigate hazards that can be introduced in the requirements, design, development, testing, installation, commissioning, operation and maintenance and disposal of a system. Events that should trigger a hazard analysis are:
- Concept definition
- Requirements review
- Design review
- Design change review
- Installation and commissioning plan review
- Operating and support plan review
- Decommissioning plan review.
A Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) is conducted in the early stages of a project. Its objectives are to:
- Identify known hazards
- Determine the cause(s) of the hazards
- Determine the effects of the hazards
- Determine the probability that an accident will be caused by a hazard
- Establish initial design and procedural requirements to eliminate or control hazards.
A PHA does NOT:
- Describe the details of how the hazards will be avoided or mitigated
- Generate detailed safety requirements
- Create strategies for implementing safety requirements.
The following items may be input into the hazard analysis process:
- System Description - a description of the system under development and the context under which it is to be used (e.g. functional model)
- Safety Incident Logs - incorporating experience gained from previous operation of the same or similar systems
- Preliminary Hazard List - this is a list of hazards determined in a previous analysis
- Hazard Checklist - this may exist for various industries that have codified the causes of safety incidents with the same or similar equipment
- Customer Requirements - any pre-existing requirements specifications and concept documents
- Regulatory Requirements - constraints imposed by regulatory agencies
- People at risk - A list of people who may be put at risk by the system (e.g. general public, environment and workers).
A hazard analysis is performed with the following steps:
- Define objectives
- Define scope
- Define and describe the system in terms of system boundaries and information to be used in the analysis
- Identify the hazards
- Collect data. For example historical data, related standards and code of practice, scientific tests and experimental results.
- Perform qualitative ranking of hazards based on their potential effects and their likelihood
- Identify causal factors
- Identify preventive or corrective measures and general design criteria and controls.
Hazards may be realized or unrealized. A realized hazard has happened in the past and can therefore be identified from experience. An unrealized hazard is a potential for a hazardous situation that has not happened in the past but can be recognized by analyzing the characteristics of an environment or failure modes of equipment items.
Hazard analysis techniques include:
- Function Failure Analysis
- Event Tree Analysis
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- Fault Tree Analysis
- Cause-consequence Diagrams
- Hazard and Operability Studies.
- See also:Hazard Discovery Techniques
The outcomes of the hazard analysis are documented in the Hazard Analysis Report and a Hazard Log.
Typical outputs are:
- A summary of the process and techniques used
- A consolidated hazard list
- Hazard causes
- The assumptions made during the analysis activity
- Risk assessment.
The outputs of a hazard analysis are used to:
- Develop systems safety requirements
- Prepare design descriptions
- Prepare test plans
- Prepare operational instructions
- Prepare management plans.
Member Comments |
25 Comments |
20 member ratings |
|
✭ ✭ ✭ ✭ ✩
|
|

|



